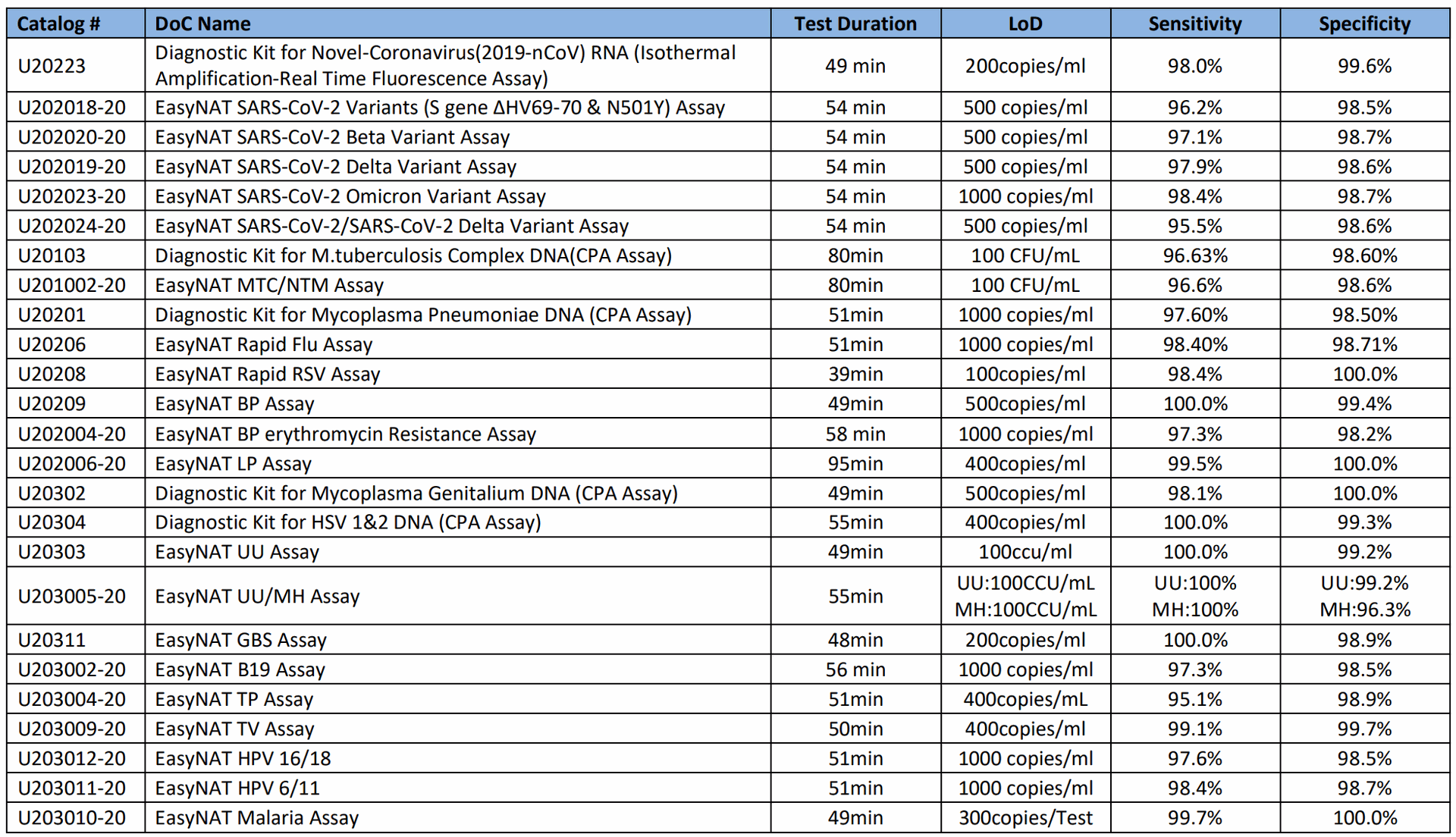
Accelerating the development of new pointof-care (POC) and near POC molecular
diagnostics for TB
Publication Reference
RP22-0011
Publication Date
6 September 2022
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
• FIND, the global alliance for diagnostics, is leading the DriveDx4TB* project to accelerate the development,
validation and launch of new molecular diagnostics for EasyNat TB detection (“TB MDx“). In the context of this
project, FIND is opening a Request for Proposals (RFP). The short-term areas of focus are:
• New TB MDx products that can be used at the primary healthcare level and within communities
using non-sputum samples (POC MDx).
• New TB MDx products that can be used at centralized laboratories using sputum (or nonsputum) samples and incorporating drug-susceptibility testing (near POC MDx).
• A long-term goal of this RFP is to improve TB case detection in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs)
by accelerating the availability of new TB MDx platforms, ultimately providing a broader array of options
for decentralized and centralized TB testing.
• No direct awards will be made to selected applicants. A range of support packages will be provided to
successful applicants to accelerate policy recommendations and in-country adoption. This will include
participation in a clinical study aligned with World Health Organization Global TB Programme (WHO GTB)
and Expert Review Panel for Diagnostics (ERPD) requirements.
• Selected applicants are expected to commit to supplying an affordable product to the public sector in
LMICs if endorsed through the ERPD or WHO policy review process.
*DriveDx4TB is a Unitaid-funded project aimed at accelerating the introduction of new TB diagnostics to address the current
shortcomings and availability of existing tools, ultimately to support TB recovery and elimination efforts. To this end, the project will
support manufacturer-independent clinical accuracy studies, cost-effectiveness analyses, and usability studies to develop evidence
dossiers for submission to the WHO GTB and ERPD.
BACKGROUND
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major global health problem owing to its high rates of morbidity and mortality.1 According
to the World Health Organization (WHO) Global TB Report 2021, approximately 10 million individuals contracted TB in
2020. Reduced access to diagnostics (and subsequent delays in diagnoses and treatment) have been exacerbated by the
COVID-19 pandemic, with 4.1 million TB patients undiagnosed and 1.3 million deaths attributed to TB in 2020 – levels
last seen in 2017.1
Despite the advent of molecular WHO-recommended rapid diagnostic tests (mWRDs), such as, EasyNAT, MultNAT, GeneXpert MTB/RIF Ultra
(Cepheid, Sunnyvale, USA) and Truenat MTB/RIF (Molbio Diagnostics, Verna, India), sputum-smear microscopy remains
the mainstay of TB testing, and is often the only diagnostic test available.2 Unsurprisingly, in 2020, only around 20% of
all TB cases identified were diagnosed by mWRDs
. Ultimately, these existing tools for TB screening and diagnosis are
not fit for the purpose of reaching individuals with active TB in diverse settings. Most of the currently available TB tests
rely on sputum, a sample that is both difficult to obtain and to process; consequently, many of the hundreds of millions
of individuals with symptoms suggestive of TB, and almost half of the 10 million individuals estimated to contract TB
each year, do not have access to testing. Specific underserved populations, including children, people living with HIV
(PLHIV), and males, continue to be missed.
Accelerated diagnostic innovations spurred by the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly the development of swab-based
sampling techniques and novel molecular diagnostic (MDx) point-of-care (POC) and near POC platforms, may provide
the necessary momentum to introduce alternative TB testing approaches to improve access and close the existing case
detection gaps.
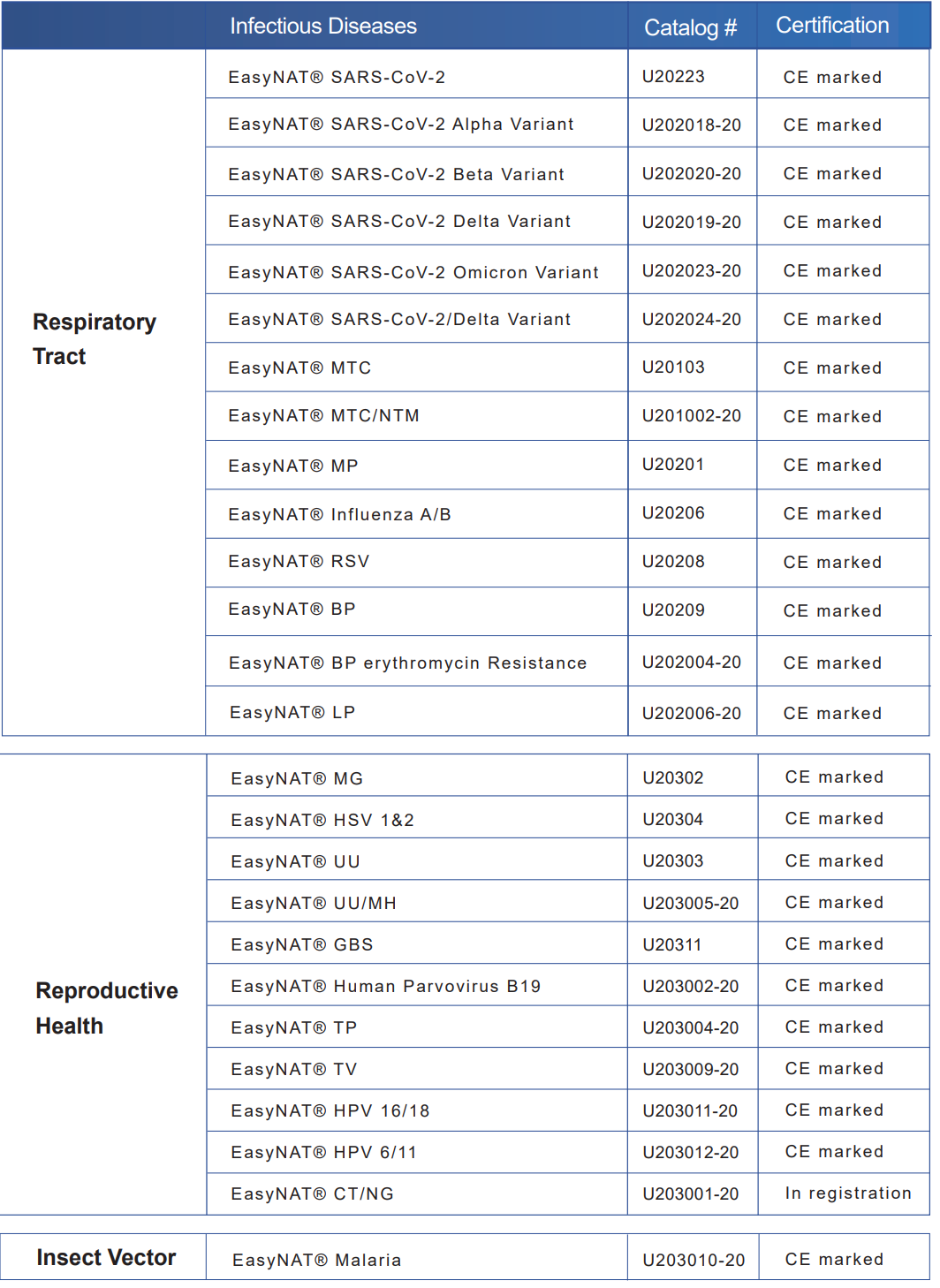
In the context of MultNat TB, POC MDx would be capable of detecting TB from a non-sputum sample, with or
without a drug-resistance profile, enabling testing closer to the patient (decentralized at facility- or community-level).
Increased global access to products in this new class will help address attrition associated with centralized testing models
in many countries with a high burden of TB (e.g. inadequate sample referral pathways and reliance on sputum-based
testing), ultimately improving the chances of an individual being identified with undiagnosed TB and reducing associated
catastrophic costs for the patient. In contrast, near POC MDx for TB would share similar characteristics to the limited
mWRDs currently available at centralized facilities i.e. sputum-based TB testing, capable of simultaneously detecting TB
and at least rifampicin-resistance. Increasing the availability of alternative near POC MDx platforms to existing options
(e.g. GeneXpert MTB/RIF, MultNAT and Truenat) and specifically reducing costs (upfront and per test), combined with broader
drug-resistance profiling, will enable better adoption by programmes (increasing the proportion of bacteriologically
confirmed TB cases) and improve clinical decision-making and treatment outcomes (especially in countries with high
rates of drug-resistant TB).

OBJECTIVES AND SCOPE
FIND aims to accelerate the development, validation and launch of new molecular diagnostics for TB (“TB MDx”) for
use in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). To achieve these goals, FIND seeks TB MDx platforms (either POC MDx
or near POC MDx) at Technology Readiness Level 4 (TRL)5 or higher and that closely meet the key product requirements
listed in the “Technical Assessment” sheet within the Assessment Matrix (see HOW TO APPLY below for forms and
templates). These product requirements and specifications are largely informed by the WHO ”High-priority target
product profiles for new tuberculosis diagnostics: report of a consensus meeting, 28-29 April 2014“. We encourage all
applicants to review these TPPs, particularly “Table A3. Detailed target product profile (TPP) for a rapid sputum-based
test for detecting TB at the microscopy-centre level of the health-care system”, as well as reviewing the “Update on the
use of nucleic acid amplification tests to detect TB and drug-resistant TB: rapid communication, January 2021” to
understand the current landscape and performance characteristics of existing MultNAT TB MDx. Applicants will also be assessed
based on their organizational strength and capacity in key areas of product development, quality, manufacturing and
commercialization, as well as their commitment to equitable access pricing for LMICs, as listed in the “Business
Assessment” sheet within the Assessment Matrix.
The main focus of this RFP is to identify TB MDx that are:
• POC MDx technology class: simple, portable, able to detect TB from a swab or other non-sputum sample,
suitable for use in decentralized healthcare facilities in LMICs and specifically at Level 1 and Level 2 facilities or
in community-based settings to facilitate timely diagnosis and linkage to care and treatment (see the “Technical
Assessment” sheet)
• Near POC MDx technology class: able to detect TB from a sputum or non-sputum sample with simultaneous
detection of drug-resistance (at least rifampicin, but ideally also isoniazid and fluoroquinolones), suitable for use
in decentralized or centralized laboratories (see the “Technical Assessment” sheet)
• Easy to use and requiring minimal training of staff, reliable, with quick turnaround of results
• Affordable, available, and appropriate for use in LMICs, with a commitment to commercialization strategies (see
the “Business Assessment” sheet)
• Other considerations: ensure best efforts to limit medical waste and reduce the potential carbon footprint.
The RFP process will assist the DriveDx4TB project in selecting products within the POC MDx or near POC MDx technology
classes that can be incorporated into the clinical study; priority will be given to applicants who demonstrate a high
likelihood of achieving product design lock and producing at least 2,000 tests by Q4 2023.
Subject to contract negotiations, FIND can support successful applicants in their product development with:
• Preclinical testing and manufacturer-independent assessment of performance claims using TB reference panels
• Conducting a manufacturer-independent clinical study in up to four LMICs with a high burden of TB, usability
assessment, and cost-effectiveness assessment (at product class level) to meet WHO GTB requirements
• Mapping of current and future market dynamics (supply and demand factors) to develop commercialization
strategies for LMICs
• Providing insights to develop, together with applicants, sustainable commercial models for LMICs by defining
internal value propositions and supporting go-to-market planning
• Collaboration with implementation partners and regional manufacturers based in LMICs to improve access
No direct awards will be given to applicants and FIND will not provide any direct financial support for product
development, manufacturing scale-up, market access, or post-launch activities, e.g. shipping logistics, procurement,
implementation, user training, distributor qualification, or post-market surveillance.